Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics and Optoelectronics; State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials and Devices, Guangdong Engineering Technology Research and Development Center of Special Optical Fiber Materials and Devices, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Fiber Laser Materials and Applied Techniques, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China
2 Research Institute of Future Technology, South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510006, China
We report a high-stability ultrafast ultraviolet (UV) laser source at 352 nm by exploring an all-fiber, all-polarization-maintaining (all-PM), Yb-doped femtosecond fiber laser at 1060 nm. The output power, pulse width, and optical spectrum width of the fiber laser are 6 W, 244 fs, and 17.5 nm, respectively. The UV ultrashort pulses at a repetition rate of 28.9 MHz are generated by leveraging single-pass second-harmonic generation in a 1.3-mm-long BiB3O6 (BIBO) and sum frequency generation in a 5.1-mm-long BIBO. The maximum UV output power is 596 mW. The root mean square error of the output power of UV pulses is 0.54%. This laser, with promising stability, is expected to be a nice source for frontier applications in the UV wavelength window.
all-polarization-maintaining fiber ultrafast fiber laser UV laser Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(3): 031404

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 South China University of Technology, School of Physics and Optoelectronics, Guangzhou, China
2 South China University of Technology, State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials, Guangzhou, China
3 South China University of Technology, Guangdong Engineering Technology Research and Development Center of Special Optical Fiber Materials and Devices, Guangzhou, China
4 South China University of Technology, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Fiber Laser Materials and Applied Techniques, Guangzhou, China
5 South China Normal University, Research Institute of Future Technology, Guangzhou, China
Laser processing with high-power ultrashort pulses, which promises high precision and efficiency, is an emerging new tool for material structuring. High repetition rate ultrafast laser highlighting with a higher degree of freedom in its burst mode is believed to be able to create micro/nanostructures with even more variety, which is promising for electrochemical applications. We employ a homemade high repetition rate ultrafast fiber laser for structuring metal nickel (Ni) and thus preparing electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) for the first time, we believe. Different processing parameters are designed to create three groups of samples with different micro/nanostructures. The various micro/nanostructures not only increase the surface area of the Ni electrode but also regulate local electric field and help discharge hydrogen bubbles, which offer more favorable conditions for HER. All groups of the laser-structured Ni exhibit enhanced electrocatalytic activity for HER in the alkaline solution. Electrochemical measurements demonstrate that the overpotential at 10 mA cm - 2 can be decreased as much as 182 mV compared with the overpotential of the untreated Ni (-457 mV versus RHE).
high repetition rate ultrafast laser burst mode operation nickel electrocatalyst hydrogen evolution reaction Advanced Photonics Nexus
2023, 2(5): 056009

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics and Optoelectronics, State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials and Devices, Guangdong Engineering Technology Research and Development Center of Special Optical Fiber Materials and Devices, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Fiber Laser Materials and Applied Techniques, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China
2 Research Institute of Future Technology, South China Normal University, Guangzhou, China
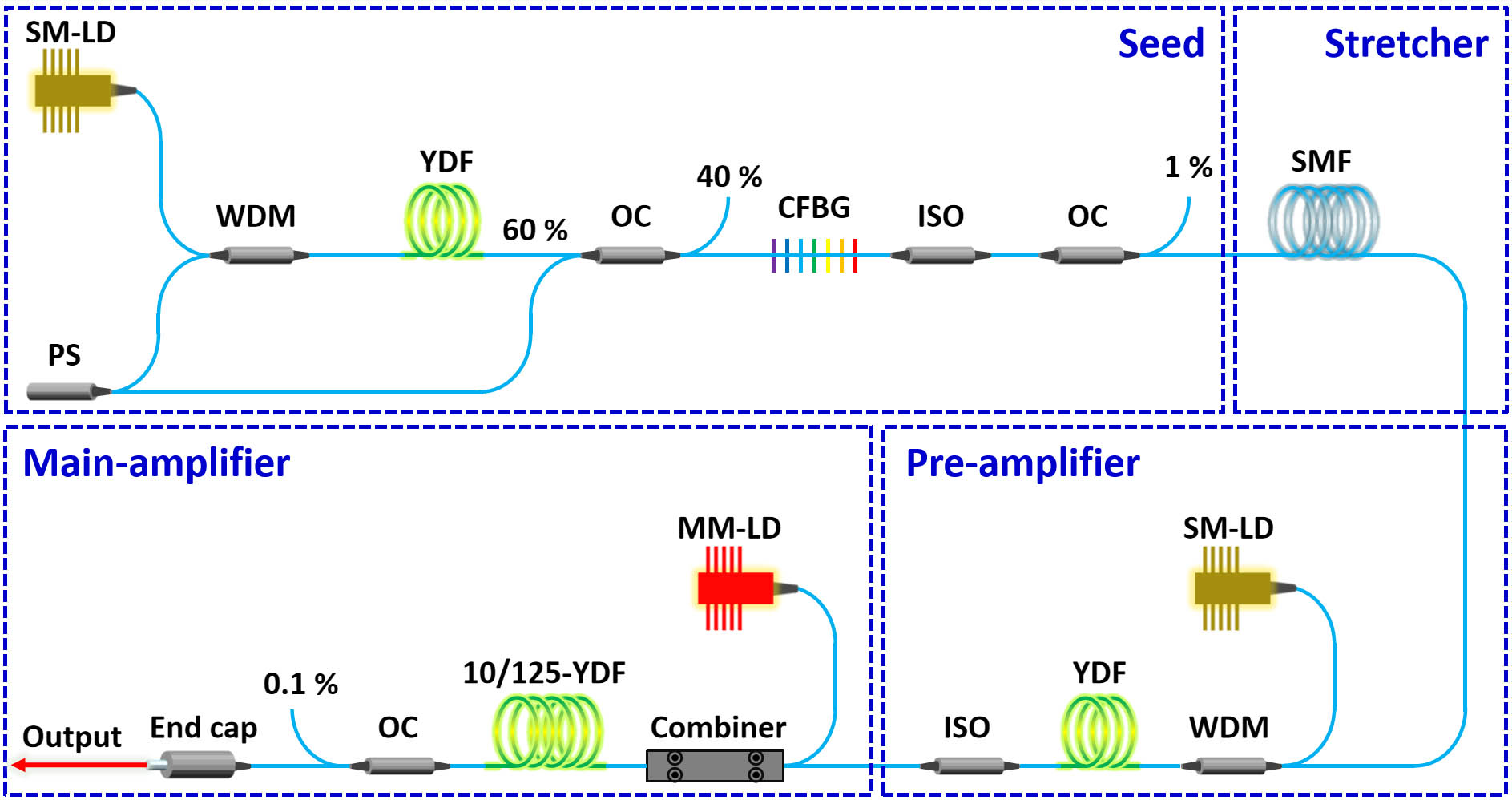
In this work, we present a high-power, high-repetition-rate, all-fiber femtosecond laser system operating at 1.5 $\unicode{x3bc}$ m. This all-fiber laser system can deliver femtosecond pulses at a fundamental repetition rate of 10.6 GHz with an average output power of 106.4 W – the highest average power reported so far from an all-fiber femtosecond laser at 1.5 $\unicode{x3bc}$ m, to the best of our knowledge. By utilizing the soliton-effect-based pulse compression effect with optimized pre-chirping dispersion, the amplified pulses are compressed to 239 fs in an all-fiber configuration. Empowered by such a high-power ultrafast fiber laser system, we further explore the nonlinear interaction among transverse modes LP01, LP11 and LP21 that are expected to potentially exist in fiber laser systems using large-mode-area fibers. The intermodal modulational instability is theoretically investigated and subsequently identified in our experiments. Such a high-power all-fiber ultrafast laser without bulky free-space optics is anticipated to be a promising laser source for applications that specifically require compact and robust operation.
high-power femtosecond fiber laser high repetition rate intermodal modulational instability nonlinear pulse compression High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2023, 11(4): 04000e50
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150001, China
2 Key Laboratory of Micro-Nano Optoelectronic Information System, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, Harbin 150001, China
3 Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
4 Heilongjiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Plasma Physics and Application Technology, Harbin 150001, China
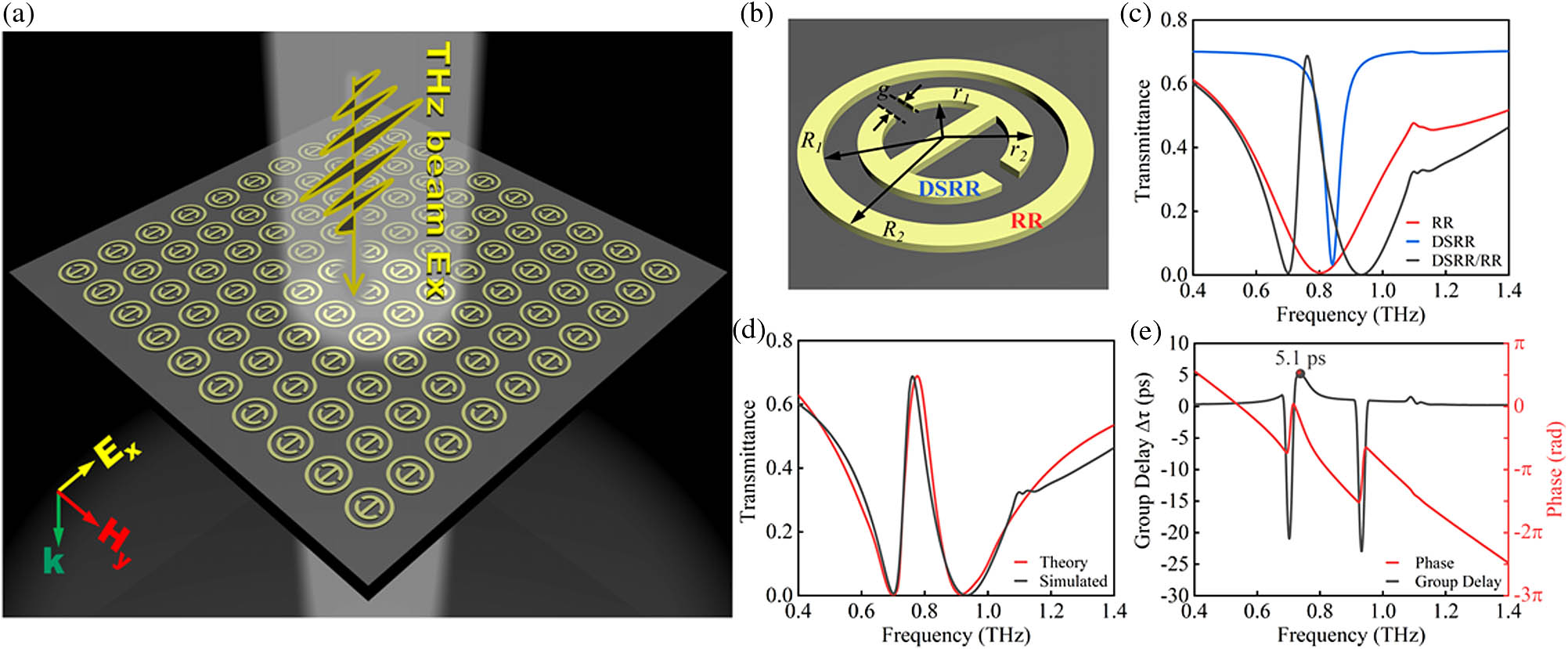
We present a hybrid coupling scheme of a magnetic toroidal and electric dipole metasurface with suppressed radiation loss, which can produce the tunable plasmon-induced transparency (PIT) with an enhanced slow-light effect in the terahertz regime. The terahertz metasurface is constructed by nesting a dual-split ring resonator (DSRR) inside a ring resonator (RR) to exploit the destructive coherence of hybrid electromagnetic mode coupling at the PIT resonance. The polarization-dependence excitation performs the active tunability of a PIT-induced group slowing down by rotating the polarization angle, experimentally achieving a maximum group delay of 3.5 ps. Furthermore, the modified terahertz metasurface with a four-split ring resonator (FSRR) nested in an RR is prepared on photoconductive silicon, demonstrating the pump-controllable group delay effect at the PIT resonance. The large group delay from 2.2 to 0.9 ps is dynamically tunable by adjusting the pump power. The experimental results are in good accord with the theoretical simulations.
Photonics Research
2023, 11(4): 494
1 天津大学精密仪器与光电子工程学院激光与光电子研究所,天津 300072
2 天津大学光电信息技术教育部重点实验室,天津 300072
报道了基于掺Yb3+石英有源光纤的高峰值功率脉冲单频激光主振荡功率放大器(MOPA)。实验研究了主放大器中有源光纤长度对脉冲单频激光峰值功率、受激布里渊散射(SBS)阈值和光-光转换效率的影响,为优化激光器的转换效率和抑制SBS效应提供了依据。当使用的有源光纤长度为0.9 m时,21 W泵浦功率下脉冲宽度为2.4 ns、重复频率为20 kHz的1064.4 nm脉冲单频激光的平均输出功率为4.37 W,且没有明显的连续波放大自发辐射(ASE)成分,对应的单脉冲能量为0.22 mJ,峰值功率可达91 kW。最大输出功率时脉冲单频激光光谱线宽为279 MHz,光信噪比为45 dB,光束质量因子M2为1.44。
光纤光学 脉冲单频激光 光纤激光器 主振荡功率放大器 受激布里渊散射
1 哈尔滨工业大学物理学院, 哈尔滨 150001
2 微纳光电信息系统理论与技术工信部重点实验室, 哈尔滨 150001
3 山西大学极端光学协同创新中心, 太原 030006
采用顶部籽晶助熔法制备0.15% (摩尔分数)Fe掺杂的KTa1-xNbxO3晶体, 测试了晶体介电性能、电致应变性能分布、组分分布和电畴结构。结果表明: 数字全息是一种有效表征材料应变空间分布的方法, Fe: KTN晶体电致应变性能呈现不均匀分布的特性, 室温下外加电场为435 V/mm时, 晶体应变最大值为0.05%, 有3/4区域应变在0.02%附近。Fe: KTN晶体的应变分布与组分分布、电畴结构之间存在联系, 室温低于晶体Curie温度时, 晶体Nb元素含量少的区域电畴结构小, 具有更大的电致应变。
铁掺杂钽铌酸钾晶体 介电性能 电致应变 组分分布 电畴结构 ferrum doped potassium tantalum niobate crystal dielectric properties electric-field-induced strain component distribution domain structure
西安理工大学自动化与信息工程学院,陕西 西安 710048
与特定波长处的高吸收率设计不同,3~5 μm宽波长范围内超导纳米线单光子探测器的光吸收设计需要更好地兼顾吸收率的峰值大小和带内平坦度。为此,一方面采用超窄NbN纳米线/SiO2腔/分布式布拉格光栅(DBR)来构建基于非对称法布里-珀罗(F-P)腔结构的正面对光器件初始模型;另一方面将SiO2腔、DBR的高折射率层和低折射率层这3个厚度作为优化对象,以3~5 μm波长范围内光吸收率的最小值作为优化目标,使用粒子群算法对初始模型进行优化。结果显示,相比于上下腔双谐振波长耦合的思路,基于非对称F-P腔结构并采用了高折射率差DBR的单层NbN纳米线探测器设计,在目标波长范围内光吸收率的最小值提高了40.2%,带内平坦度提高了59.2%。在此基础上的双层NbN纳米线探测器结构不仅可以进一步提高光吸收率的最小值,而且可以在不追求特定波长处高吸收率的情况下将吸收率的最大值提升至0.97以上,达到与双谐振波长耦合方法相当的水平。
探测器 超导纳米线单光子探测器 宽带光吸收 非对称法布里-珀罗腔 分布式布拉格光栅 3~5 µm 激光与光电子学进展
2022, 59(17): 1704002
1 天津大学精密仪器与光电子工程学院,天津 300072
2 天津大学光电信息技术教育部重点实验室,天津 300072
报道了基于混合增益光纤实现的1064 nm高能量单频掺Yb3+百纳秒脉冲全光纤激光器。当主放大级的泵浦功率为13 W时,获得了最大0.59 mJ的脉冲能量,重复频率为5 kHz,脉冲宽度为104 ns。主放大级采用芯径分别为35 μm和50 μm的掺Yb3+光纤级联作为增益介质,以此来提高受激布里渊散射阈值和激光信噪比。为了保证转换效率,对有源光纤长度和盘绕方式进行了优化,实现了较好的光束质量,最大脉冲能量时光束质量为1.50,光谱线宽为40 MHz。
激光器 光纤激光器 脉冲激光器 激光放大器 受激布里渊散射 中国激光
2022, 49(13): 1301005
天津大学 天津纳米颗粒与纳米系统国际研究中心, 天津300072
光电探测器因可将光信号转换为电信号而被广泛地应用于视频成像、光通信、生物医学成像和运动检测等方面。但由于所采用的传统光电探测器材料对其性能带来的局限性和日益增长的新需求之间的矛盾, 使得寻找新的材料迫在眉睫。近年来新兴的二维材料为制备更高性能的探测器提供了全新的材料研究平台, 其中石墨烯以其独特的电学、光学与热学特性成为下一代高性能光子学最有希望的候选材料之一。本文系统地综述了不同光响应机制下石墨烯基光电探测器研究现状, 并在此基础上对当下不同石墨烯基光电器件发展前景进行了细致的讨论和展望。
石墨烯 光电探测器 响应机制 研究进展 graphene photodetector response mechanism research progress

1 石河子大学食品学院, 新疆 石河子 832003
2 石河子大学机械电气工程学院, 新疆 石河子 832003
酿酒葡萄中的总酚含量是影响葡萄品质的重要指标, 也是影响葡萄酒质量的关键因素。 为了快速准确地检测赤霞珠葡萄的总酚含量, 利用近红外光谱技术结合GA-ELM预测模型对赤霞珠葡萄总酚含量进行预测研究。 试验采用5个收获期(每期采集40串, 每串取10个)的赤霞珠葡萄, 采集200组葡萄的12 500~4 000 cm-1波段范围内的近红外光谱。 基于福林酚比色法原理对赤霞珠葡萄的总酚含量进行测定, 使用SPXY算法将样品按照3:1比例分为校正集和预测集, 共计150个校正集和50个预测集。 分别采用多元散射(MSC)、 标准正态变换(SNV)、 数据中心化(MC)、 移动窗口平滑(MA)和一阶导数+SG方法对原始光谱进行预处理, 优选出最佳的预处理方法为MSC。 并进一步采用竞争性自适应重加权算法(CARS)、 遗传算法(GA)、 联合区间偏最小二乘算法(si-PLS)和连续投影算法(SPA)分别对光谱波段进行提取, 经对比分析发现CARS提取的69个特征波长数据能有效提高模型的稳定性和预测结果。 在MSC预处理和特征波长提取的基础上, 引入极限学习机(ELM)算法, 建立赤霞珠葡萄总酚含量的预测模型, 在总酚含量预测过程中, 采用遗传算法(GA)对ELM模型进行优化, 并探究了不同的激活函数和隐含层神经元个数对GA-ELM模型预测能力的影响, 确定最优的激活函数为Sigmoidal, 最优的神经元个数为50个。 最后, 将ELM和GA-ELM模型的预测能力进行对比, 结果显示GA-ELM模型的预测能力高于ELM模型的预测能力, 其中MSC+CARS+GA-ELM模型预测能力最好, 校正相关系数(Rc)为0.901 7, 预测相关系数(Rp)为0.901 3, 校正均方根误差(RMSEC)为2.112 4, 预测均方根误差(RMSEP)为1.686 8, 剩余预测偏差(RPD)为2.308 0。 研究结果表明: 利用近红外光谱技术结合变量优选建立的GA-ELM模型可实现对赤霞珠葡萄的总酚含量的预测, 为赤霞珠葡萄品质的检测奠定了理论基础。
变量优选 赤霞珠葡萄 总酚 极限学习机 近红外光谱 Variable optimization Cabernet sauvignon grapes Total phenol Extreme learning machine Near infrared spectroscopy 光谱学与光谱分析
2021, 41(7): 2036





